
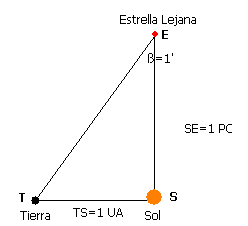
Penumbra - During an eclipse, the area of partial shadow. Partial eclipse - When the moon partially blocks the sun or the Earth's shadow partially the Moon. ~ - A unit of distance equal to 3.26 light-years, and the the distance at which a star would have a parallax of 1 second of arc. Pair production The process in which two photons of electromagnetic radiation give rise to a particle-anti-particle pair. ~ The distance at which a star must lie in order that its measured parallax is exactly 1 arc second, equal to 206,000 A.U. A ~ is the distance at which 1 AU subtends an angle of 1 arcsec. This is because its definition is closely related to a method of measuring the distances between stars. Many astronomers prefer to use ~s (abbreviated pc) to measure distance to stars.

The use of the ~ has been carried into the 21st Century because of historical inertia and because its use avoids the application of conversion factors - i.e., 3.Ī ~ is a unit of length used to measure the distances between objects located beyond our solar system, and is equal to 3.26 light-years (19 trillion miles/31 trillion km). The radius of the Earth's orbit equals one astronomical unit (AU), so an object that is one ~ distant is 206,265 AU (or 3.26 light-years) away. One ~ is the distance to an object whose parallax angle is one arcsecond. Unit of distance at which a star would have a parallax of 1 second of arc from a planet of exactly 1 astronomical unit (AU) distance from its primary.
#Parsec to km professional
A ~ is equal to about 3.26 light-years (31 trillion kilometres or 19 trillion miles) in length.Ī ~ is the unit for expressing distances to stars and galaxies, used by professional astronomers. One ~ is the distance at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one arcsecond. Ī parsec is defined as the distance from the Sun which would result in a parallax of 1 second of arc as seen from Earth.Ī ~ (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure large distances to objects outside the Solar System. The parsec was defined to be the distance at which 1 AU (perpendicular to the line of sight) subtends an angle of 1 arcsecond. The rest of the problems are similar so I leave them to you to work out.Distances to the closest stars can be determined through measurement of their trigonometric parallax. Always convert to the same length unit (or mass unit, or whatever).

Attention: the biggest mistake most students make is being careless about meters and kilometers. The distance from the Sun to the Earth is 1.5 x 10 8 km (actually it’s 1.496 x 10 8 km on average, but two digits is sufficient for most calculations in this class), or 1.5 x 10 11 m, since there are 10 3 m/ 1 km.

How long does it take for light to reach the earth from the Sun (in seconds)? Another way to do it is illustrated in the next problem.ġ2.
#Parsec to km Pc
Perhaps easiest is to convert from parsecs to light years,ģ.5 pc x 3.26 ly/pc = 11.4 ly and by definition, light takes one year to travel one light-year, so it would take 11.4 years. (b) How long (in years) does it take light from Procyon to reach Earth? (note, I only care about 10% accuracy in answers, so 1.1 x 10 14 or even 1 x 10 14 km would be acceptable). From the book (and I would give you this information on a quiz or test), 1 pc (parsec) = 3.09 x 10 13 km. Solution: This is simple unit conversion. (a) What is the distance to Procyon in kilometers? The bright star Procyon is 3.50 pc from Earth. I will only work a couple, as these are simple word problems.ġ1. Solutions : answers are found in the back of the book. Homework #1: Chapter 1, question 1-10 (review), 11-18 (advanced). Homework #1: Chapter 1, question 1-10 (review), 11-18 (advanced)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
